In the realm of customer management, CRM for client management stands tall as a transformative force, empowering businesses to forge lasting relationships with their valued clientele. Dive into this comprehensive guide and discover how CRM can revolutionize your client acquisition, retention, and support strategies, propelling your business to new heights of success.
From streamlining sales processes to harnessing data analytics for actionable insights, CRM is the key to unlocking a world of possibilities in client management. Join us as we delve into the intricacies of CRM, exploring its myriad benefits and uncovering the secrets to its effective implementation.
Types of CRM Systems
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems come in various types, each offering unique advantages and disadvantages. Understanding the different types can help businesses choose the most suitable option for their specific needs and goals.
The three main types of CRM systems are cloud-based, on-premise, and open-source.
Cloud-based CRM Systems
Cloud-based CRM systems are hosted on remote servers, accessible through the internet. This eliminates the need for businesses to maintain their own hardware and software infrastructure.
- Advantages:
- Cost-effective: No upfront hardware or software costs, and pay-as-you-go pricing models.
- Scalable: Easily adjust the system to meet changing business needs.
- Accessible: Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Disadvantages:
- Internet dependency: Requires a stable internet connection for access.
- Security concerns: Data stored on third-party servers may raise security concerns.
On-premise CRM Systems
On-premise CRM systems are installed and run on the business’s own hardware and software infrastructure.
- Advantages:
- Control and security: Businesses have complete control over their data and security measures.
- Customization: Systems can be tailored to meet specific business requirements.
- Disadvantages:
- High upfront costs: Requires significant investment in hardware, software, and IT resources.
- Maintenance and updates: Ongoing maintenance and software updates are the responsibility of the business.
Open-source CRM Systems
Open-source CRM systems are free and open to use, with the source code available for customization.
- Advantages:
- Cost-effective: No licensing fees or ongoing subscription costs.
- Customization: Developers can modify the source code to suit specific needs.
- Disadvantages:
- Technical expertise: Requires technical expertise to install, configure, and maintain the system.
- Limited support: May have limited technical support compared to proprietary systems.
CRM for Client Acquisition
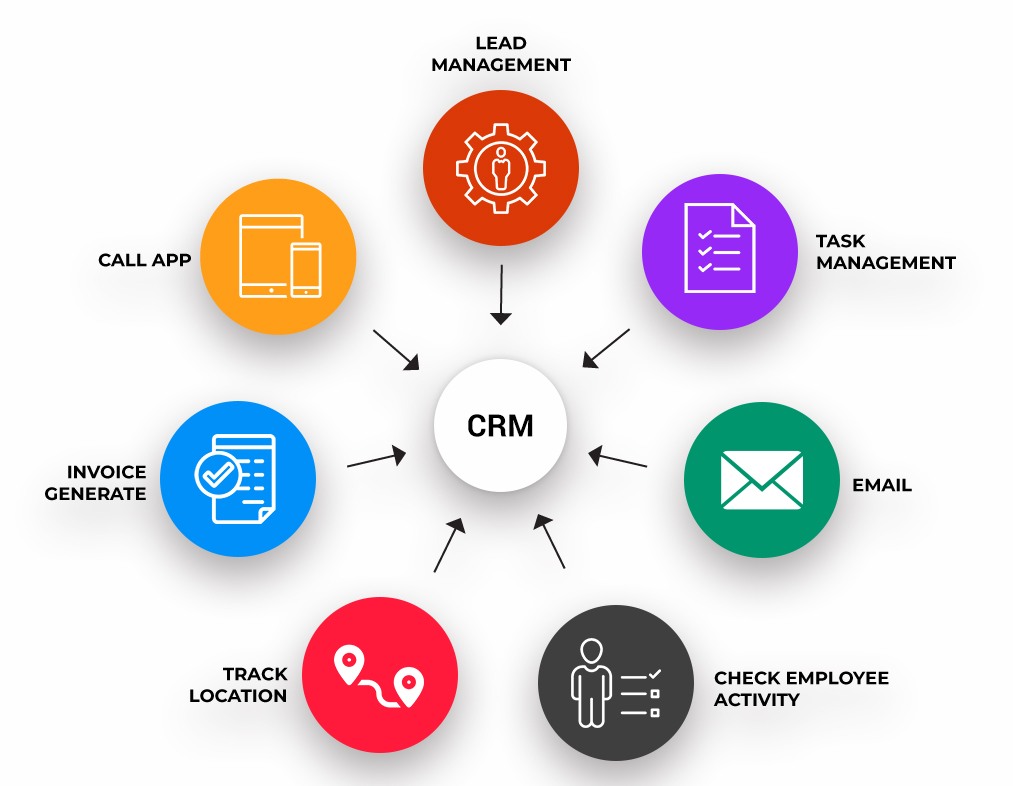
Customer relationship management (CRM) is an essential tool for businesses of all sizes. It can help you manage your customer interactions, track your sales pipeline, and generate new leads. In this section, we’ll discuss how CRM can help you acquire new clients.
Lead Generation
CRM can help you generate leads in a number of ways. You can use it to:
- Create and manage lead capture forms
- Track your website traffic and identify potential leads
- Purchase lead lists from third-party providers
- Attend industry events and trade shows
Lead Nurturing
Once you’ve generated leads, you need to nurture them until they’re ready to buy. CRM can help you do this by:
- Automating email campaigns
- Providing personalized content
- Tracking lead activity
- Scoring leads based on their engagement
By nurturing your leads, you can increase the chances of converting them into customers. CRM can help you automate many of the tasks involved in lead nurturing, so you can focus on other aspects of your business.
CRM for Client Retention

Customer relationship management (CRM) is a powerful tool for retaining existing clients and building strong, long-lasting relationships with them. By leveraging CRM data and insights, businesses can identify at-risk customers, understand their needs, and proactively address any issues or concerns they may have.
This helps prevent customer churn and ensures that clients remain loyal to the brand.
Here are some best practices for using CRM to improve customer satisfaction and loyalty:
Personalize Communication
CRM allows businesses to personalize communication with clients based on their individual preferences, purchase history, and past interactions. By sending targeted messages, offering tailored recommendations, and providing relevant content, businesses can create a more personalized and engaging experience for their clients, increasing their satisfaction and loyalty.
Track Customer Interactions
CRM provides a central repository for all customer interactions, including phone calls, emails, social media messages, and in-person visits. This allows businesses to track the entire customer journey and identify areas where improvements can be made. By understanding the touchpoints and pain points in the customer experience, businesses can optimize their processes and deliver a more seamless and satisfying experience.
Provide Excellent Customer Service
CRM empowers customer service teams with the tools and information they need to provide exceptional support to clients. By having access to a complete view of the customer’s history, preferences, and past interactions, customer service representatives can quickly resolve issues, answer questions, and go the extra mile to ensure customer satisfaction.
This helps build trust and loyalty, and encourages clients to continue doing business with the company.
Reward Customer Loyalty
CRM can be used to implement loyalty programs and reward clients for their repeat business. By offering points, discounts, exclusive offers, and other incentives, businesses can encourage clients to stay loyal and make repeat purchases. Loyalty programs help foster a sense of community and appreciation, and they can significantly increase customer retention rates.
Monitor Customer Feedback
CRM can be used to collect and analyze customer feedback through surveys, reviews, and social media monitoring. This feedback provides valuable insights into customer satisfaction, areas for improvement, and potential risks. By actively listening to customer feedback and taking action to address any concerns, businesses can demonstrate that they value their clients and are committed to delivering a positive experience.
CRM for Sales Management
CRM is a powerful tool that can help businesses streamline their sales processes and improve their overall sales performance. By providing a centralized platform for managing customer data, tracking interactions, and automating tasks, CRM can help sales teams:
- Shorten sales cycles:By providing easy access to customer information and automating tasks such as lead qualification and scheduling appointments, CRM can help sales teams shorten their sales cycles and close deals faster.
- Increase sales productivity:CRM can help sales teams increase their productivity by providing them with tools to manage their pipelines, track their progress, and identify opportunities for improvement.
- Improve customer satisfaction:CRM can help sales teams improve customer satisfaction by providing them with a better understanding of their customers’ needs and preferences. This can lead to more personalized and relevant sales interactions, which can result in increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Tips for Using CRM to Manage Sales Pipelines and Track Customer Interactions
Here are a few tips for using CRM to manage sales pipelines and track customer interactions:
- Use a CRM system that is designed for sales management.There are many different CRM systems on the market, so it is important to choose one that is specifically designed for sales management. This will ensure that the system has the features and functionality that you need to manage your sales pipeline and track customer interactions effectively.
- Implement a sales process that is supported by your CRM system.Your sales process should define the steps that your sales team needs to take to close a deal. Once you have defined your sales process, you can configure your CRM system to support it. This will help your sales team to stay on track and to close deals more efficiently.
- Use your CRM system to track all of your customer interactions.This includes tracking phone calls, emails, meetings, and social media interactions. By tracking all of your customer interactions, you can get a better understanding of your customers’ needs and preferences. This information can then be used to personalize your sales interactions and to improve customer satisfaction.
- Use your CRM system to generate reports on your sales pipeline and customer interactions.These reports can help you to identify trends and to make informed decisions about your sales strategy.
CRM for Marketing Automation
CRM systems can be integrated with marketing automation tools to streamline marketing campaigns and improve customer engagement. This integration allows businesses to automate tasks such as lead generation, lead nurturing, and email marketing, freeing up marketing teams to focus on more strategic initiatives.
By leveraging CRM data, marketing teams can create targeted marketing campaigns that are tailored to the specific needs and interests of their customers. This can lead to improved ROI, increased conversion rates, and enhanced customer loyalty.
Integration of CRM and Marketing Automation
- Lead generation:CRM systems can capture lead information from various sources, such as website forms, email campaigns, and social media. This information can then be used to create targeted marketing campaigns.
- Lead nurturing:CRM systems can track lead activity and engagement, allowing marketing teams to identify leads that are most likely to convert into customers. These leads can then be nurtured through automated email campaigns and other marketing initiatives.
- Email marketing:CRM systems can be integrated with email marketing platforms to automate email campaigns. This allows marketing teams to send personalized emails to leads and customers based on their behavior and preferences.
CRM for Customer Support
CRM is crucial for delivering exceptional customer support by streamlining and organizing customer interactions. It provides a centralized platform that empowers support teams to manage inquiries efficiently and resolve issues promptly.
Managing Customer Inquiries
- Centralized Inbox:CRM consolidates all customer inquiries from various channels (email, phone, chat) into a single inbox, giving support teams a comprehensive view of customer interactions.
- Ticket Prioritization:CRM allows teams to prioritize inquiries based on urgency, ensuring that critical issues are addressed first.
- Automated Response:CRM can automate responses to common inquiries, freeing up support agents to focus on complex issues.
Issue Resolution
- Customer History:CRM provides a detailed history of each customer’s interactions, enabling support agents to understand their context and provide personalized assistance.
- Knowledge Base:CRM integrates with knowledge bases, allowing agents to quickly access relevant articles and solutions to resolve issues.
- Collaboration:CRM facilitates collaboration between support agents, allowing them to consult with subject matter experts or escalate issues to the appropriate team.
CRM for Data Analytics: Crm For Client Management

CRM systems are equipped with robust data analytics capabilities that empower businesses to gather, analyze, and interpret valuable customer data. This data can provide deep insights into customer behavior, preferences, and trends, enabling businesses to make informed decisions and enhance their customer engagement strategies.
CRM data analytics involves collecting and analyzing customer data from various touchpoints, including sales interactions, marketing campaigns, customer support inquiries, and social media platforms. By leveraging advanced analytics techniques, businesses can uncover patterns, identify trends, and gain actionable insights that drive better decision-making.
Data Analytics Use Cases
- Customer Segmentation:CRM data analytics helps businesses segment customers based on demographics, behavior, and preferences. This enables targeted marketing campaigns and personalized customer experiences.
- Predictive Analytics:CRM systems use predictive analytics to forecast customer behavior, identify potential churn risks, and optimize sales and marketing efforts.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV) Analysis:CRM data analytics helps businesses calculate the lifetime value of each customer, enabling them to prioritize high-value customers and allocate resources accordingly.
- Customer Journey Mapping:CRM data analytics provides insights into the customer journey, allowing businesses to identify touchpoints, optimize the customer experience, and reduce friction.
- Trend Analysis:CRM data analytics helps businesses identify emerging trends in customer behavior, preferences, and industry dynamics, enabling them to adapt their strategies accordingly.
CRM Implementation and Best Practices
Implementing a CRM system effectively requires a well-defined plan and adherence to best practices. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you navigate the process and ensure successful adoption and utilization.
Key Steps in CRM Implementation
- Define Business Objectives:Clearly Artikel the specific goals and objectives you aim to achieve with CRM implementation.
- Select a CRM System:Evaluate different CRM solutions based on your business needs, budget, and technical capabilities.
- Data Migration:Transfer relevant data from existing systems or sources into the new CRM system.
- Customization and Configuration:Tailor the CRM system to align with your specific business processes and workflows.
- Go Live:Launch the CRM system and monitor its performance to ensure it meets expectations.
li> User Training:Provide comprehensive training to users to ensure they understand the system’s functionality and best practices.
Best Practices for CRM Adoption and Utilization
- Secure Buy-In from Stakeholders:Engage key stakeholders throughout the implementation process to gain their support and commitment.
- Foster User Adoption:Encourage users to actively participate in the implementation and provide feedback to enhance the system’s effectiveness.
- Establish Data Governance:Implement clear policies and procedures to ensure data accuracy, consistency, and accessibility.
- Monitor and Measure Success:Track key metrics and conduct regular evaluations to assess the CRM system’s impact on business outcomes.
- Continuous Improvement:Regularly review and update the CRM system to adapt to evolving business needs and technological advancements.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Real-world examples of successful CRM implementations provide valuable insights into the tangible benefits and outcomes achieved by organizations.
These case studies showcase how businesses have leveraged CRM systems to enhance client interactions, streamline processes, and drive growth.
Salesforce Success Story
- Salesforce, a leading CRM provider, implemented its own CRM system to manage its vast customer base.
- By leveraging Salesforce’s CRM capabilities, the company gained a 360-degree view of its customers, enabling personalized interactions and tailored marketing campaigns.
- Salesforce’s CRM system also streamlined sales processes, improved collaboration, and increased sales productivity.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Success Story, Crm for client management
- AWS, a cloud computing giant, implemented a CRM system to manage its rapidly growing customer base.
- The CRM system provided AWS with a centralized platform to track customer interactions, manage sales pipelines, and provide personalized support.
- AWS’s CRM implementation resulted in improved customer satisfaction, increased sales conversions, and enhanced customer loyalty.
Concluding Remarks
![]()
In conclusion, CRM for client management is not merely a tool but a strategic investment that empowers businesses to elevate their customer interactions. By embracing the transformative power of CRM, organizations can cultivate loyal customer relationships, drive sales growth, and achieve unparalleled success in today’s competitive business landscape.
Q&A
What are the key benefits of CRM for client management?
CRM empowers businesses to streamline client interactions, enhance communication, and gain valuable insights into customer behavior, leading to improved client satisfaction, increased sales, and reduced costs.
How does CRM assist in client acquisition?
CRM provides tools for lead generation, lead nurturing, and campaign management, enabling businesses to attract and convert potential clients into loyal customers.
What role does CRM play in customer retention?
CRM helps businesses retain existing clients by providing a centralized platform for managing customer interactions, tracking customer preferences, and identifying opportunities for personalized engagement.
How can CRM enhance sales management?
CRM streamlines sales processes by providing tools for managing sales pipelines, tracking customer interactions, and forecasting sales performance, empowering sales teams to close deals faster and increase revenue.
What are the data analytics capabilities of CRM systems?
CRM systems offer robust data analytics capabilities that enable businesses to gain valuable insights into customer behavior, identify trends, and make informed decisions to improve customer experiences and drive business growth.
