Delve into the realm of CRM ERP tools, a transformative suite of solutions designed to streamline business processes, enhance customer relationships, and drive operational efficiency. These powerful tools empower organizations to gain a comprehensive view of their operations, enabling informed decision-making and unparalleled growth.
CRM (Customer Relationship Management) and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems work in synergy to provide a holistic approach to business management. CRM tools focus on nurturing customer interactions, while ERP systems streamline internal operations, from supply chain management to financial reporting.
Overview of CRM and ERP Tools: Crm Erp Tools
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) tools are essential software solutions for businesses of all sizes. They provide a centralized platform to manage customer interactions, streamline business processes, and improve overall efficiency.
CRM systems focus on managing customer data and interactions. They help businesses track customer touchpoints, preferences, and purchase history. This information can be used to personalize marketing campaigns, improve customer service, and increase sales.
ERP systems, on the other hand, provide a comprehensive view of a business’s operations. They integrate various business functions, such as finance, inventory management, and human resources. This allows businesses to automate processes, reduce costs, and improve decision-making.
Key Features and Functionalities of CRM and ERP Tools
- CRM Features:
- Contact management
- Lead generation
- Marketing automation
- Customer support
- Sales forecasting
- ERP Features:
- Financial management
- Inventory management
- Supply chain management
- Human resources management
- Project management
Benefits of Using CRM and ERP Tools, Crm erp tools
- Improved customer relationships:CRM systems help businesses build stronger relationships with customers by providing a centralized view of their interactions.
- Increased sales:CRM systems can help businesses identify and track potential customers, automate sales processes, and improve customer service.
- Reduced costs:ERP systems can help businesses automate processes, reduce waste, and improve efficiency.
- Improved decision-making:ERP systems provide businesses with a comprehensive view of their operations, which can help them make better decisions.
- Increased productivity:CRM and ERP tools can help businesses streamline their processes and improve productivity.
Limitations of Using CRM and ERP Tools
- Cost:CRM and ERP systems can be expensive to implement and maintain.
- Complexity:CRM and ERP systems can be complex to implement and use.
- Data security:CRM and ERP systems contain sensitive customer and business data, which can be a security risk.
- Integration:CRM and ERP systems may not integrate well with other business systems.
- Resistance to change:Employees may resist using CRM and ERP systems, which can hinder their adoption.
Comparison of CRM and ERP Tools

CRM (Customer Relationship Management) and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) tools are both essential for businesses of all sizes. However, there are some key similarities and differences between the two types of systems.
CRM systems are designed to manage customer interactions and relationships. They track customer data, such as contact information, purchase history, and support interactions. CRM systems can help businesses improve customer service, increase sales, and build stronger customer relationships.
ERP systems, on the other hand, are designed to manage all aspects of a business’s operations. They integrate data from different departments, such as finance, manufacturing, and human resources. ERP systems can help businesses improve efficiency, reduce costs, and make better decisions.
Key Features and Functionalities
- CRM systemstypically include features such as contact management, lead tracking, sales forecasting, and customer support.
- ERP systemstypically include features such as financial management, inventory management, supply chain management, and human resource management.
Benefits of CRM and ERP Tools
- CRM systemscan help businesses improve customer service, increase sales, and build stronger customer relationships.
- ERP systemscan help businesses improve efficiency, reduce costs, and make better decisions.
Using CRM and ERP Tools Together
CRM and ERP systems can be used together to improve business processes. For example, a CRM system can be used to track customer interactions and identify opportunities for upselling or cross-selling. This information can then be used by an ERP system to create sales orders and invoices.
By integrating CRM and ERP systems, businesses can gain a complete view of their customers and operations. This can help them make better decisions, improve customer service, and increase sales.
Selection and Implementation of CRM and ERP Tools
The selection and implementation of CRM and ERP tools are crucial for businesses seeking to optimize their operations and customer interactions. Here are key factors to consider and steps involved in the process:
Key Factors for Selection
- Business Objectives:Define specific goals and requirements that the tools should address.
- Industry-Specific Needs:Consider tools tailored to the unique requirements of your industry.
- Scalability:Ensure the tools can adapt to future growth and changes in business needs.
- Integration Capabilities:Evaluate how well the tools integrate with existing systems and data sources.
- Vendor Reputation and Support:Research the vendor’s experience, track record, and support offerings.
Steps for Implementation
Implementing CRM and ERP tools involves a structured approach:
- Planning:Establish project scope, timeline, and resource allocation.
- Data Migration:Transfer data from legacy systems to the new tools.
- Configuration and Customization:Tailor the tools to specific business requirements.
- User Training:Provide comprehensive training to ensure effective tool utilization.
- Testing and Go-Live:Conduct thorough testing and launch the tools in a controlled environment.
Best Practices for Successful Implementation
- Stakeholder Involvement:Engage key stakeholders throughout the process to ensure buy-in and adoption.
- Change Management:Implement strategies to manage resistance and promote user acceptance.
- Data Integrity:Ensure data accuracy and consistency during migration and ongoing operations.
- Continuous Improvement:Regularly evaluate and refine the tools to meet evolving business needs.
- Vendor Collaboration:Maintain open communication and collaboration with the vendor for support and optimization.
Use Cases and Applications of CRM and ERP Tools
CRM and ERP tools find widespread applications across various industries and business functions, enabling organizations to streamline operations, enhance customer relationships, and drive business growth.
Industries Using CRM and ERP Tools
- Manufacturing:Streamlining production processes, inventory management, and customer order fulfillment.
- Retail:Enhancing customer experience, managing inventory, and optimizing supply chain.
- Healthcare:Improving patient care, managing medical records, and billing.
- Financial Services:Automating financial processes, managing customer relationships, and mitigating risk.
- Technology:Tracking software development, managing customer support, and automating billing.
Business Functions Using CRM and ERP Tools
- Sales and Marketing:Managing customer relationships, tracking leads, and automating marketing campaigns.
- Customer Service:Providing personalized support, resolving customer queries, and managing customer feedback.
- Operations:Managing inventory, optimizing supply chain, and automating production processes.
- Finance and Accounting:Automating financial processes, managing accounts payable and receivable, and generating financial reports.
- Human Resources:Managing employee records, tracking performance, and automating payroll.
Case Studies of Successful CRM and ERP Implementations
- Salesforce:Salesforce’s CRM platform helped increase sales productivity by 25% for a leading telecommunications company.
- SAP:SAP’s ERP system enabled a global manufacturing company to reduce inventory costs by 15% and improve production efficiency.
- Oracle:Oracle’s CRM and ERP solutions helped a healthcare provider improve patient satisfaction by 20% and reduce administrative costs.
Latest Trends and Emerging Technologies in CRM and ERP
- Cloud Computing:Cloud-based CRM and ERP systems offer flexibility, scalability, and reduced IT costs.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):AI-powered tools automate tasks, improve customer experience, and provide predictive insights.
- Internet of Things (IoT):IoT devices connect to CRM and ERP systems, providing real-time data and automating processes.
- Data Analytics:Advanced analytics tools help businesses gain insights from CRM and ERP data, improving decision-making.
Integration of CRM and ERP Tools
Integrating CRM and ERP systems offers numerous benefits, including improved customer data management, streamlined business processes, and enhanced collaboration between departments. By connecting these two systems, businesses can gain a holistic view of their customers, track interactions, and manage orders more efficiently.
Challenges and Best Practices of CRM and ERP Integration
Integrating CRM and ERP systems can be complex and requires careful planning. Common challenges include data mapping, system compatibility, and user adoption. Best practices for successful integration include:*
- Clearly defining integration goals and objectives
- Choosing compatible software solutions
- Mapping data fields accurately
- Testing the integration thoroughly
- Training users on the new system
Examples of Successful CRM and ERP Integrations
Many businesses have successfully integrated CRM and ERP systems to improve their operations. Some notable examples include:*
- Salesforce and NetSuite
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 and SAP ERP
- Oracle Siebel CRM and Oracle E-Business Suite
These integrations have enabled businesses to improve customer satisfaction, increase sales, and streamline operations.
Future of CRM and ERP Tools
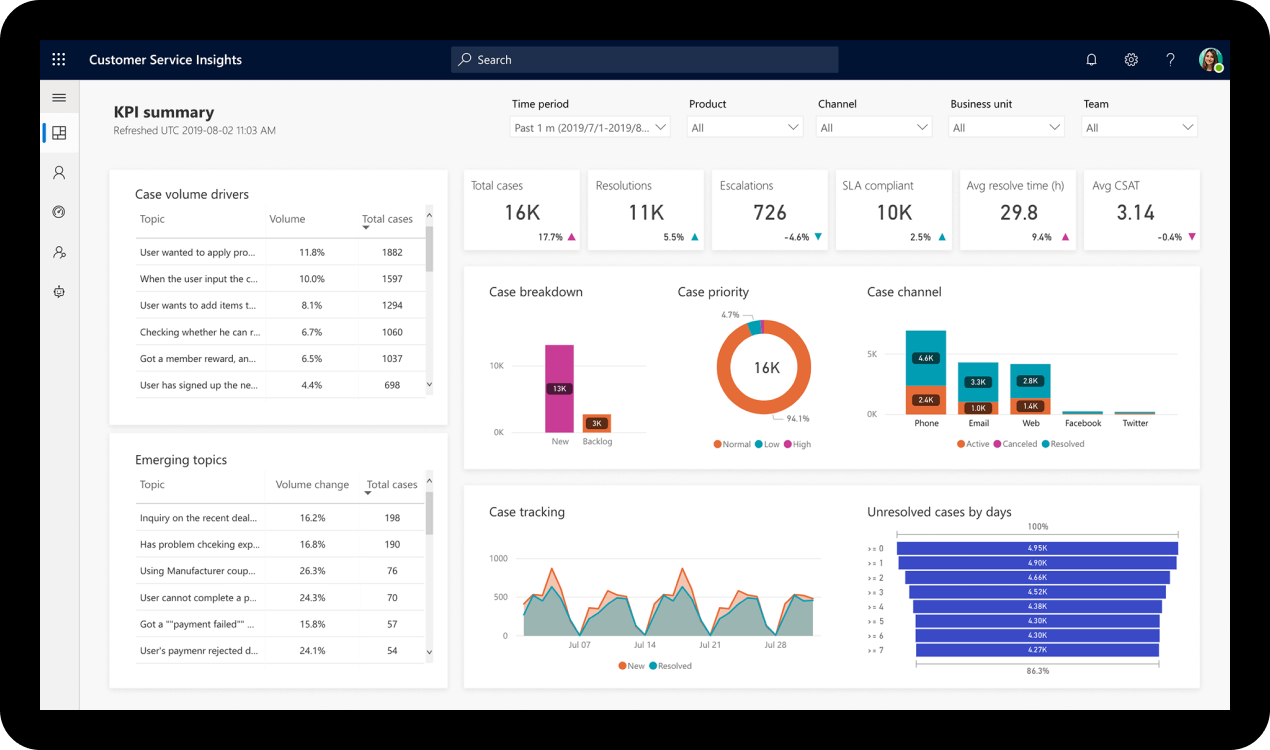
The future of CRM and ERP tools holds exciting advancements that will revolutionize business operations. Emerging technologies such as AI, machine learning, and cloud computing are shaping the next generation of these systems.
AI-powered CRM and ERP tools will enhance customer engagement and streamline business processes. Machine learning algorithms will analyze vast amounts of data to provide personalized recommendations, automate tasks, and predict future trends.
Impact of AI and Machine Learning
- Personalized customer experiences
- Automated lead scoring and segmentation
- Predictive analytics for sales forecasting
Role of Cloud Computing
- Scalability and flexibility
- Reduced infrastructure costs
- Enhanced collaboration and accessibility
Insights into the Future
- Seamless integration of CRM and ERP systems
- Real-time data analytics and reporting
- Increased automation and efficiency
Closing Notes

In conclusion, CRM ERP tools have revolutionized the way businesses operate, providing a competitive edge through improved efficiency, enhanced customer experiences, and data-driven insights. As technology continues to evolve, these tools will undoubtedly play an increasingly vital role in driving business success.
Popular Questions
What are the key benefits of using CRM ERP tools?
CRM ERP tools offer numerous benefits, including improved customer satisfaction, increased operational efficiency, enhanced data management, and better decision-making.
How do CRM and ERP systems differ?
CRM systems focus on managing customer relationships, while ERP systems manage internal business operations. CRM tools track customer interactions, while ERP systems manage inventory, supply chain, and financial data.
What are the challenges of implementing CRM ERP tools?
Implementing CRM ERP tools can be challenging due to factors such as data integration, user adoption, and cost. However, careful planning and professional implementation can mitigate these challenges.
