Best CRM for architects is more than just software; it’s a strategic tool transforming how architectural firms manage projects, clients, and overall workflow. Finding the right CRM can significantly improve efficiency, boost client satisfaction, and ultimately contribute to the firm’s success. This exploration delves into the essential features, software comparisons, and integration considerations crucial for selecting the ideal CRM solution tailored to the unique needs of architectural practices, regardless of size or specialization.
From managing complex project timelines and intricate client communication to seamlessly integrating with industry-specific software like CAD and BIM, a well-chosen CRM streamlines operations, minimizes administrative burdens, and frees architects to focus on what they do best: design. This guide will navigate you through the key considerations, helping you make an informed decision that optimizes your firm’s potential.
Defining Architectural CRM Needs
Choosing the right Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is crucial for architectural firms of all sizes. A well-implemented CRM can streamline workflows, improve client communication, and ultimately boost profitability. This section explores the specific needs of architectural firms when selecting a CRM, highlighting the key functionalities and addressing the unique challenges they face.
Key Functionalities of an Architectural CRM
Architectural firms require CRMs with specific capabilities beyond basic contact management. These functionalities are essential for managing complex projects, fostering strong client relationships, and maintaining efficient internal operations. Critical features include robust contact management, detailed project tracking with milestones and deadlines, document management capabilities for storing blueprints and contracts, and seamless integration with other essential software like CAD programs and accounting systems.
Furthermore, effective communication tools, such as integrated email and scheduling features, are paramount. Finally, reporting and analytics capabilities are necessary to track key performance indicators (KPIs) like project profitability and client satisfaction.
Challenges Faced by Architects and CRM Solutions
Architects face unique challenges in managing projects and client communications. Complex projects often involve multiple stakeholders, intricate design processes, and frequent revisions. Maintaining clear communication with clients, consultants, and contractors is vital to avoid delays and misunderstandings. Furthermore, managing large volumes of project-related documents, ensuring version control, and maintaining a centralized repository for easy access are significant hurdles.
A CRM system can effectively address these challenges by providing centralized project management tools, secure document storage, and streamlined communication channels. For example, a CRM can facilitate timely updates on project progress, manage approvals, and distribute important documentation efficiently.
CRM Requirements: Small Firms vs. Large Enterprises
The CRM requirements differ significantly between small architectural firms and large enterprises. Small firms often prioritize affordability and ease of use, focusing on core functionalities like contact management, basic project tracking, and proposal generation. They may opt for simpler, cloud-based solutions that require minimal setup and IT support. In contrast, large architectural firms often require more sophisticated systems with advanced features like workflow automation, extensive reporting capabilities, and integration with multiple software platforms.
They may need on-premise solutions or highly customizable cloud-based systems to accommodate their complex workflows and large data volumes. The scalability and customizability of the CRM become crucial considerations for large enterprises.
Essential CRM Features Comparison
The following table compares essential features across different CRM categories, tailored to the needs of architectural firms.
| Feature | Basic CRM | Mid-Range CRM | Enterprise CRM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contact Management | Basic contact details, limited segmentation | Advanced contact details, robust segmentation, custom fields | Advanced contact management, detailed relationship mapping, integrated social media data |
| Project Management | Basic task management, simple timelines | Detailed project tracking, milestones, Gantt charts, resource allocation | Advanced project management, workflow automation, resource optimization, real-time progress tracking |
| Proposal Generation | Basic template support | Advanced template customization, automated proposal generation | Automated proposal generation, integrated with design software, client approval workflows |
| Document Management | Basic file storage | Version control, secure document sharing, access control | Centralized document repository, robust search functionality, integrated with CAD software |
Top CRM Features for Architects

A robust CRM system is crucial for architectural firms to manage projects, clients, and resources effectively. Choosing a CRM with the right features can significantly improve efficiency, collaboration, and ultimately, profitability. This section will delve into the key features that architectural firms should prioritize when selecting a CRM solution.
Project Management Capabilities in Architectural CRMs
Effective project management is paramount in architecture. A CRM system should offer tools to track project phases, assign tasks, manage deadlines, and monitor progress. For example, a CRM could allow architects to create custom project workflows, assigning tasks to specific team members with due dates and associated documents. This ensures everyone is aware of their responsibilities and deadlines, minimizing the risk of delays.
Real-time progress tracking enables proactive identification of potential roadblocks, allowing for timely interventions. Visual dashboards can display project timelines, resource allocation, and budget status, providing a clear overview of project health. Integrating project management features directly within the CRM eliminates the need for disparate software, streamlining communication and collaboration.
Document Management and Collaboration Tools
Architectural projects involve a vast number of documents – blueprints, specifications, contracts, correspondences, and more. A CRM with integrated document management capabilities allows for centralized storage, version control, and easy access for all relevant parties. This eliminates the chaos of scattered files and email chains, reducing the risk of errors and delays caused by miscommunication or lost documents.
Collaboration tools within the CRM, such as shared annotation features or integrated communication channels, further enhance teamwork. For instance, architects can review and comment on designs directly within the CRM, facilitating efficient feedback loops and accelerating the design process.
Tracking Project Milestones, Deadlines, and Budgets
Precise tracking of project milestones, deadlines, and budgets is essential for successful project delivery and financial health. A well-designed CRM allows architects to set custom milestones, assign them deadlines, and track progress against those deadlines. Budget tracking features enable monitoring of expenses against allocated budgets, providing early warnings of potential overruns. Automated alerts and notifications can be set up to inform team members of approaching deadlines or budget concerns, enabling proactive management and mitigation of risks.
This level of detail allows for accurate forecasting and resource allocation, contributing to improved project profitability.
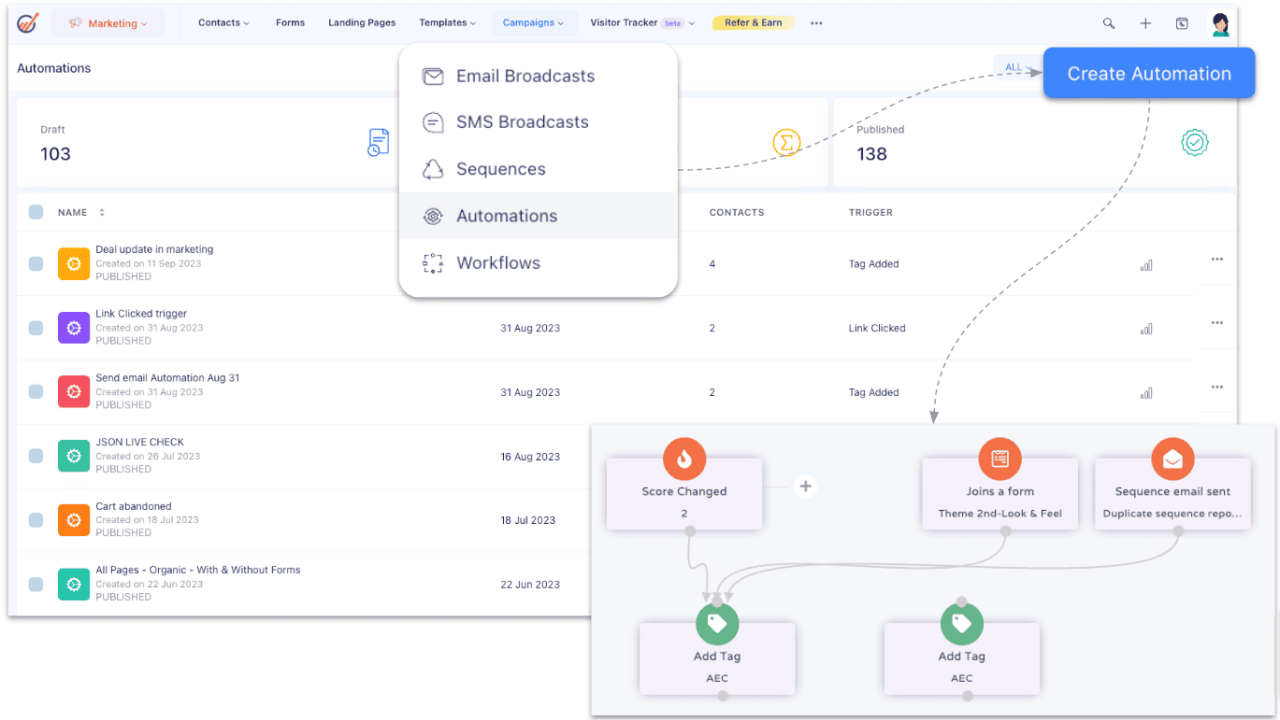
Workflow Diagram: CRM Integration with Architectural Software
The following describes a workflow illustrating CRM integration with other architectural software:Imagine a diagram showing a central CRM system at the heart of the workflow. Arrows point from the CRM to various architectural software packages, such as AutoCAD, Revit (BIM software), and rendering software. Another arrow points from the CRM to a project management platform like Asana or Trello.
Another arrow leads to accounting software. The diagram would visually represent how data, such as project details, client information, and document versions, flows seamlessly between these systems. For example, a project created in Revit (BIM) would automatically update the project status and relevant information within the CRM, including budget allocation and timeline updates. Similarly, invoices generated in accounting software would update the project’s financial status within the CRM.
This integrated approach ensures all stakeholders have access to the most current and accurate information.
CRM Software Comparison for Architects
Choosing the right CRM can significantly streamline operations for architectural firms. This section compares three leading CRM platforms – HubSpot, Salesforce, and Monday.com – based on their suitability for architectural practices, highlighting key features and considerations for selection. Each platform offers unique strengths, and the optimal choice depends on the specific needs and size of the architectural firm.
CRM Feature Comparison for Architectural Firms
The following table compares HubSpot, Salesforce, and Monday.com across several key criteria relevant to architectural firms. Note that pricing can vary significantly based on the chosen plan and number of users. Scalability refers to the CRM’s ability to adapt to a growing business, and integration capabilities refer to its compatibility with other software commonly used in architectural workflows.
| Feature | HubSpot | Salesforce | Monday.com |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing | Starts at $450/month for Professional Plan (with limitations); higher tiers for advanced features. | Highly variable, depending on edition (Essentials, Professional, Enterprise, etc.) and number of users; generally more expensive than HubSpot. | Starts at $24/month per user for the Basic Plan; higher tiers for increased functionality and features. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable; easily adapts to growing user bases and data volumes. | Extremely scalable; designed for large enterprises and can handle massive amounts of data. | Scalable, but potentially requires more manual configuration for very large firms. |
| Integration Capabilities | Integrates with many popular business tools, including project management software and design platforms (though some may require custom integrations). | Extensive integration capabilities through its AppExchange; integrates with a vast ecosystem of third-party applications. | Integrates with a range of apps, including popular project management tools and file sharing services. |
| Ease of Use | Generally considered user-friendly, with an intuitive interface. | Can have a steeper learning curve, particularly for users unfamiliar with CRM software. | Visually appealing and relatively intuitive, especially for users comfortable with visual project management tools. |
| Customization Options | Offers robust customization options, allowing tailoring to specific business needs. | Highly customizable; extensive options for workflow automation and data management. | Offers good customization, particularly through its automation features and board customization. |
| Customer Support | Provides various support channels, including documentation, community forums, and paid support options. | Offers comprehensive support resources, including extensive documentation, training, and dedicated support teams. | Provides support via documentation, community forums, and email. |
Client Communication, Project Collaboration, and Proposal Creation
Each CRM can be effectively utilized for managing these key aspects of architectural practice.HubSpot: Facilitates client communication through email marketing, automated workflows, and a centralized contact database. Project collaboration can be enhanced through integration with project management tools. Proposals can be created and tracked within the system, monitoring their progress and ensuring timely follow-up.Salesforce: Leverages its robust features for sophisticated client relationship management, including detailed contact information, communication history, and opportunity tracking.
Its extensive integration capabilities allow seamless project collaboration with various design and project management tools. Salesforce can be customized to create a streamlined proposal creation and management process.Monday.com: Utilizes visual project boards for intuitive project collaboration, enabling easy task assignment, progress tracking, and communication among team members. Client communication can be managed through integrated messaging and file sharing.
Proposals can be organized and tracked within project boards, ensuring transparency and efficient workflow.
Integration with Architectural Software and Tools
Seamless integration between a CRM and other architectural software is crucial for maximizing efficiency and minimizing redundant data entry in an architectural firm. A well-integrated system streamlines workflows, improves collaboration, and ultimately contributes to better project management and client satisfaction. The ability to connect various software solutions minimizes the risk of errors and delays inherent in manual data transfer.Effective integration allows for the smooth flow of information between different software platforms used throughout the architectural design process.
This interconnectedness fosters better collaboration among team members, improves project visibility, and allows for more informed decision-making. For instance, a project’s progress, as tracked in a project management tool, can be automatically updated in the CRM, providing clients with real-time insights. Similarly, financial data from accounting software can be seamlessly integrated, giving architects a clear view of project profitability.
Benefits of CRM Integration with Other Architectural Software
Integrating a CRM with project management tools, accounting software, and communication platforms offers numerous advantages. Project management tools, when linked to the CRM, allow for the tracking of project milestones, deadlines, and resource allocation, directly within the client relationship context. This provides a holistic view of the project’s progress and associated client interactions. Integration with accounting software streamlines billing and expense tracking, ensuring accurate financial reporting and facilitating better financial management.
Finally, integrating with communication platforms ensures that all communication – emails, calls, and messages – is centralized and readily accessible within the client profile, providing a complete history of client interaction.
Examples of Improved Efficiency Through Integration
Imagine a scenario where a project manager updates the project timeline in their project management software. With seamless integration, this update automatically reflects in the CRM, instantly notifying the relevant team members and updating the client on the project’s progress. This eliminates the need for manual data entry and reduces the risk of inconsistencies. Similarly, if an architect closes a deal, the information is automatically transferred to the accounting software, generating an invoice and updating the project’s financial status in real-time.
This automation saves valuable time and resources, allowing architects to focus on core design and client relationship activities.
Potential Integration Challenges and Solutions
Efficient integration requires careful planning and execution. Several challenges might arise.
- Data incompatibility: Different software programs may use different data formats. Solution: Utilize APIs or middleware to bridge the gap and ensure data consistency.
- Cost of integration: Integrating multiple systems can be expensive, requiring specialized software or consultants. Solution: Carefully evaluate the cost-benefit analysis and prioritize integrations based on their impact on efficiency and profitability.
- Technical expertise: Setting up and maintaining integrated systems requires technical expertise. Solution: Engage IT professionals or utilize cloud-based solutions that offer simplified integration processes.
- Security concerns: Integrating multiple systems increases the potential for security breaches. Solution: Implement robust security measures, including data encryption and access controls, across all integrated platforms.
- Vendor lock-in: Choosing incompatible software can lead to vendor lock-in, limiting future flexibility. Solution: Select software with open APIs and cloud-based solutions to maximize flexibility and avoid vendor dependency.
Cost and ROI of Architectural CRMs

Investing in a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is a significant decision for any architectural firm. The initial cost is only one part of the equation; understanding the potential return on investment (ROI) is crucial for justifying the expense and ensuring a successful implementation. This section will explore the various pricing models available, the potential benefits leading to a positive ROI, and methods for calculating that ROI.
Architectural CRM Pricing Models
Architectural CRM software typically follows one of several pricing models. Subscription-based models are the most common, offering tiered pricing based on features, user numbers, and data storage capacity. These subscriptions are usually billed monthly or annually. Some providers offer a freemium model, providing basic functionality for free with paid upgrades for advanced features. Less common is the one-time purchase model, where the software is bought outright, but this usually lacks ongoing support and updates.
Finally, some vendors utilize a per-user, per-month model, charging based on the number of users accessing the system. The choice depends on the firm’s size, budget, and anticipated needs. A smaller firm might find a freemium or basic subscription sufficient, while a larger firm might require a more comprehensive, enterprise-level solution with a higher monthly fee.
Return on Investment (ROI) from Architectural CRMs
The ROI from implementing an architectural CRM stems primarily from improved efficiency and enhanced client satisfaction. Improved efficiency comes from streamlined workflows, automated tasks (such as email marketing and project tracking), and centralized client data access. This reduces administrative overhead, freeing up architects and staff to focus on design and client interaction. Enhanced client satisfaction results from improved communication, personalized service, and proactive project management.
Happy clients lead to repeat business, referrals, and positive reviews, contributing significantly to revenue growth. By reducing administrative time, improving project management, and fostering stronger client relationships, a CRM can directly impact the bottom line.
Calculating the ROI of an Architectural CRM, Best crm for architects
Calculating the ROI of a CRM involves comparing the costs of implementation against the anticipated benefits. Costs include the software subscription fees, implementation costs (consulting, training, data migration), and ongoing maintenance. Benefits should be quantified wherever possible. For example, if the CRM reduces administrative time by 10 hours per week per employee, this can be translated into a cost saving based on the employee’s hourly rate.
Similarly, an increase in client retention or the number of successful project bids can be expressed in terms of increased revenue. A simple ROI calculation can be expressed as:
ROI = (Net Benefits – Total Costs) / Total Costs
Let’s consider a hypothetical example: An architectural firm with 5 employees spends $1000 per month on a CRM subscription. The CRM saves them 5 hours per week per employee on administrative tasks, equivalent to $100 per employee per week ($500 total per week, or $2000 per month) in saved labor costs. Therefore:
ROI = ($2000 – $1000) / $1000 = 1.0 or 100%
This is a simplified example, and a more thorough analysis would consider other factors like increased revenue from new clients or improved project success rates.
Cost Factors and Potential Benefits of CRM Implementation
| Cost Factors | Potential Benefits | Cost Factors | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software Subscription Fees | Improved Client Communication | Implementation Costs (Training, Consulting) | Streamlined Project Management |
| Data Migration Costs | Increased Efficiency and Productivity | Ongoing Maintenance & Support | Enhanced Client Satisfaction & Retention |
| Hardware Upgrades (if needed) | Improved Collaboration & Teamwork | Staff Training Time | Better Lead Management & Conversion Rates |
| Integration with Existing Software | Data-Driven Decision Making | Increased Revenue & Profitability |
Choosing the Right CRM for Specific Needs: Best Crm For Architects

Selecting the optimal CRM for an architectural firm hinges on a careful assessment of its unique requirements. Factors such as firm size, budget, technological proficiency, and the specific type of architectural projects undertaken significantly influence the suitability of different CRM systems. A well-chosen CRM can streamline workflows, enhance client relationships, and ultimately boost profitability. Conversely, a poorly selected system can lead to inefficiencies and added costs.
Factors Influencing CRM Selection for Small vs. Large Architectural Firms
Small architectural firms often prioritize ease of use, affordability, and quick implementation. They may favor simpler, cloud-based CRM solutions with intuitive interfaces requiring minimal training. Conversely, larger firms with complex workflows and multiple projects might necessitate more robust, scalable systems offering advanced features like project management integration, extensive reporting capabilities, and potentially on-premise solutions for enhanced security and data control.
The number of users and the need for granular access controls also differ significantly.
The Importance of Firm Size, Budget, and Technological Expertise
Firm size directly correlates with the complexity of a CRM needed. A small firm with a handful of employees might find a basic contact management system sufficient, while a large firm with numerous employees, projects, and clients requires a more comprehensive system with advanced features and integrations. Budget constraints are a significant factor; cloud-based solutions typically offer more affordable subscription models compared to on-premise systems which require upfront investment in hardware and software.
Technological expertise within the firm influences the choice of CRM; firms with limited IT support might prefer user-friendly systems with readily available training and support resources.
CRM Systems Suited for Different Architectural Practices
The type of architectural practice also plays a crucial role. For instance:
- Residential Architecture: A CRM focusing on contact management, lead nurturing, and project tracking is often sufficient. Systems like HubSpot CRM or Zoho CRM could be suitable choices due to their ease of use and robust contact management features.
- Commercial Architecture: Larger, more complex projects necessitate a CRM with advanced features like project management capabilities, collaborative tools, and potentially integrations with BIM software. Salesforce Sales Cloud or Microsoft Dynamics 365 could be suitable options for their scalability and advanced functionalities.
- Landscape Architecture: A CRM with strong visual capabilities, perhaps integrating with GIS software, might be beneficial for managing site plans and client communication related to landscape designs. Systems with customizable dashboards allowing for easy visualization of project progress could be advantageous.
Decision-Making Flowchart for Selecting an Architectural CRM
A structured approach is vital to selecting the right CRM. The following flowchart can guide architects:
[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would begin with a starting point “Assess Your Firm’s Needs”. Branches would lead to questions such as: “Small Firm ( <10 employees)?", "Large Budget?", "High Technological Expertise?", "Primary Focus (Residential, Commercial, Landscape)?". Each "Yes" or "No" answer would lead to different CRM recommendations or further questions, ultimately culminating in a final decision node indicating a suitable CRM system based on the answers provided. For example, a path leading through "Small Firm", "Limited Budget", "Low Technological Expertise", and "Residential Focus" might recommend HubSpot CRM, while a path through "Large Firm", "Large Budget", "High Technological Expertise", and "Commercial Focus" might suggest Salesforce Sales Cloud.]
End of Discussion
Selecting the best CRM for your architectural firm is a pivotal decision impacting efficiency, client relations, and ultimately, profitability. By carefully considering factors such as project management capabilities, integration with existing software, and cost-effectiveness, architects can empower their practices with a streamlined workflow and enhanced client engagement. This comprehensive guide has provided a framework for evaluating various CRM options, allowing firms to choose the solution that best aligns with their specific needs and goals, paving the way for sustained growth and success.
User Queries
What is the average cost of an architectural CRM?
Costs vary widely depending on features, scalability, and vendor. Expect monthly subscription fees ranging from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, or potentially one-time purchase options.
Can a CRM help with marketing and lead generation?
Yes, many CRMs offer marketing automation features like email campaigns and lead nurturing tools, helping to improve client acquisition and retention.
How long does it typically take to implement a new CRM?
Implementation time depends on the CRM’s complexity and the firm’s size. Expect anywhere from a few weeks to several months for full setup and user training.
What are the key metrics for measuring CRM ROI?
Key metrics include increased project completion rates, improved client satisfaction scores, reduced administrative time, and enhanced lead conversion rates.